

Vol.21 (2015.06.30 화)
GSPH 소식
GSPH 학술
GSPH 단신
GSPH 동정
| CONTENTS TABLE
| GSPH 동정 | 교수진 동정
김호 교수 | 보건통계학연구실(I)
▷ Publication List
/*In press (online pressed)*/
Sanghyuk Bae et al."Non-Linear Concentration-Response Relationships between Ambient Ozone and Daily Mortality" Plos One
Yeonseung Chung, Michelle L. Bell, and Ho Kim, "Weather change, air pollution and mortality: time for an in depth analysis", Epidemiology
Takashi Yorifuji, Sanghyuk Bae, Saori Kashima, Toshihide Tsuda, Hiroyuki Doi, Yasushi Honda, Ho Kim, Yun-Chul Hong,, "Health impact assessment of PM10 and PM2.5 in twenty-seven Southeast and East Asian cities" Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.
Oh et al,” "validation of Korean coefficient for modification of diet in renal disease study equation" Korean Journal of Internal Medicine
Antonio Gasparrini, Yuming Guo, Masahiro Hashizume, Patrick Kinney, Elisaveta P. Petkova, Eric Lavigne, Antonella Zanobetti, Joel D. Schwartz, Aurelio Tobias, Michela Leone, Shilu Tong, Yasushi Honda, Ho Kim, Ben G. Armstrong, "Temporal Variation in Heat-Mortality Associations: A Multi-Country Study" Environmental Health Perspectives.
Youn-Hee Lim, Min-Seon Park, Yoonhee Kim,Ho Kim, Yun-Chul Hong, “Effects of cold and hot temperature on dehydration: a mechanism of cardiovascular burden” International Journal of Biometeorology, DOI 10.1007/s00484-014-0917-2
Youn-Hee Lim, Michelle Bell, Haidong Kan, Yasushi Honda, Yue-Liang Leon , Guo, Ho Kim, “Economic status and temperature-related mortality in Asia” International Journal of Biometeorology
Youn-Hee Lim et al., "Diurnal temperature range and short-term mortality in large US communities", International Journal of Biometeorology
Gasparrini A, Guo Y, Hashizume M, Lavigne E, Zanobetti A, Schwartz J, Tobias A, Tong S, Rocklov J, Forsberg B, Leone M, De Sario M, Bell ML, Guo YLL, Wu CF, Kan H, Yi SM, de Sousa Zanotti Stagliorio Coelho M, Saldiva PH, Honda Y, Kim H, Armstrong B "Mortality risk attributable to high and low ambient temperature: a multi-country study" The Lancet
< 주요 논문 실적 요약 정리 >

세계적인 의학 학술지 The Lancet (IF: 39.207)에 기온에 의한 기여사망을 주제로 2015. 5월 게재된 논문에 김호 교수님이 책임 연구자로 진행중인 [GRL 기후변화와 대기오염에 의한 건강영향 평가] 연구진(Ho Kim, Masahiro Hashizume, Yue-Liang Leon Guo, Chang-fu Wu, Seung-Muk Yi, Yasushi Honda)이 모두 참여하였다. 본 연구에서는 호주, 브라질, 캐나다, 중국, 이탈리아, 일본, 한국, 스페인, 스웨덴, 대만, 태국, 영국, 미국의 384개 도시에서 non-optimum temperature에 의한 기여 사망분율 및 사망자수를 추정하였다. 기온-사망간의 관계를 분석하기 위해 DLNM (distributed lag non-linear model) 기법을 사용하여 city-specific time-series Poisson regression을 수행하였으며 multivariate meta-regression을 수행하여 국가별 추정치와 전체 추정치를 산출하였다. 연구 결과, 1985-2012년 74,225,220명의 사망자 중 7.71%(95% CI: 7.43-7.91)가 non-optimum temperature에 의해 사망하였다. 국가별 기여 사망분율은 태국이 3.37%로 가장 낮았고 중국이 11%로 가장 높았다. 기온에 의한 기여사망은 고온(heat)에 의한 사망(0.42%, 0.39-0.44) 보다 저온(cold)에 의한 사망(7.29%, 7.02-7.49)이 많았다.
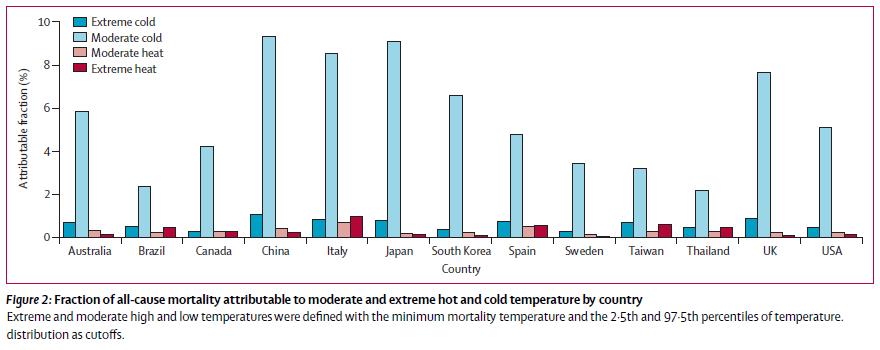
본 연구 결과는 기온에 의한 건강영향을 최소화하기 위한 보건정책의 수립 및 기후변화 시나리오의 미래영향 예측에 활용될 수 있다.